3 - Inter process communication
Inter Process Communication
Section titled “Inter Process Communication”- There are 2 kinds: SYSTEM V and POSIX in unix based
SYSTEM V
Section titled “SYSTEM V”- Introduced: Early UNIX (AT&T System V, 1983).
- APIs:
- Message Queues:
msgget,msgsnd,msgrcv,msgctl - Shared Memory:
shmget,shmat,shmdt,shmctl - Semaphores:
semget,semop,semctl
- Message Queues:
POSIX IPC
Section titled “POSIX IPC”-
Introduced: POSIX.1b (1993), more modern and portable.
-
APIs:
- Message Queues: mq_open, mq_send, mq_receive, mq_close, mq_unlink
- Shared Memory: shm_open, mmap, shm_unlink
- Semaphores: sem_open, sem_wait, sem_post, sem_unlink
Shared Memory
Section titled “Shared Memory”Without shared memory
Section titled “Without shared memory”#include <stdio.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <sys/wait.h>int main() { pid_t pid = fork(); int shared = 10; if (pid == 0) { // Child process shared += 1; printf("child: shared = %d\n", shared); } else { // Parent process shared += 2; printf("parent: shared = %d\n", shared); wait(NULL); } return 0;}OUTPUT
c@c:~/cos3105$ ./create_process2parent: shared = 12child: shared = 10Shared Memory
Section titled “Shared Memory”#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<unistd.h>#include<sys/shm.h>#include<string.h>int main(){ int i; void *shared_memory; char buff[100]; int shmid;
/* creates shared memory segment with key 2345, having size 1024 bytes. IPC_CREAT is used to create the shared segment if it does not exist. 0666 are the permisions on the shared segment */ shmid=shmget((key_t)2345, 1024, 0666|IPC_CREAT); printf("Key of shared memory is %d\n",shmid);
//process attached to shared memory segment shared_memory=shmat(shmid,NULL,0);
//this prints the address where the segment is attached with this process printf("Process attached at %p\n",shared_memory);
printf("Enter some data to write to shared memory\n"); //get some input from user read(0,buff,100); //data written to shared memory strcpy(shared_memory,buff); printf("You wrote : %s\n",(char *)shared_memory);}OUTPUT
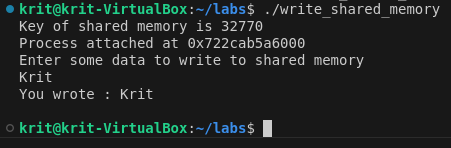
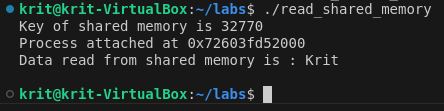
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <sys/shm.h>#include <string.h>int main(){ int i; void *shared_memory; char buff[100]; int shmid; shmid=shmget((key_t)2345, 1024, 0666); printf("Key of shared memory is %d\n",shmid); shared_memory=shmat(shmid,NULL,0); //process attached to shared memory segment printf("Process attached at %p\n",shared_memory); printf("Data read from shared memory is : %s\n",(char *)shared_memory);}OUTPUT
Parent and Child process
Section titled “Parent and Child process”#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include <sys/wait.h>#include<unistd.h>#include<sys/shm.h>#include<string.h>int main(){
void *shared_memory; char buff[100]; int shmid; pid_t pid = fork(); if (pid == 0) { printf("Child process:\n"); /* creates shared memory segment with key 2345, having size 1024 bytes. IPC_CREAT is used to create the shared segment if it does not exist. 0666 are the permisions on the shared segment */ shmid=shmget((key_t)2345, 1024, 0666|IPC_CREAT); printf("Key of shared memory is %d\n",shmid);
//process attached to shared memory segment shared_memory=shmat(shmid,NULL,0);
//this prints the address where the segment is attached with this process printf("Process %d attached at %p\n",getpid(),shared_memory);
strcpy(buff,"Krit Chomaitong"); //data written to shared memory strcpy(shared_memory,buff); printf("You wrote : %s\n",(char *)shared_memory); } else {
sleep(3); printf("Parent process:\n"); shmid=shmget((key_t)2345, 1024, 0666); printf("Key of shared memory is %d\n",shmid); shared_memory=shmat(shmid,NULL,0); //process attached to shared memory segment printf("Process %d attached at %p\n",getpid(),shared_memory); printf("Data read from shared memory is : %s\n",(char *)shared_memory); wait(NULL); } return 0;}OUTPUT
c@c:~/cos3105/tutorial$ make run./bin/myprojectChild process:Key of shared memory is 0Process 3228 attached at 0x75d7b67fc000You wrote : Krit ChomaitongParent process:Key of shared memory is 0Process 3227 attached at 0x75d7b67fc000Data read from shared memory is : Krit ChomaitongUsing mmap(POSIX)
Section titled “Using mmap(POSIX)”- Normally mmap will use
filewhich is managed by OS for shared data among processes, - But
MAP_ANONYMOUSwill not use file but use same physical memory location for share data between child and parent
#include <stdio.h>#include <sys/mman.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <sys/wait.h>
int main() { // Create shared integer int *shared_num = mmap(NULL, sizeof(int), PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED | MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0); *shared_num = 10; if (fork() == 0) { // Child process printf("Child sees: %d\n", *shared_num); *shared_num = 20; printf("Child changed it to: %d\n", *shared_num); } else { // Parent process sleep(1); // Let child run first printf("Parent sees: %d\n", *shared_num); // Will show 20 wait(NULL); }
return 0;}OUTPUT
c@c:~/cos3105$ ./create_process3Child sees: 10Child changed it to: 20Parent sees: 20Ordinary Pipes
Section titled “Ordinary Pipes”#include <stdio.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <sys/wait.h>#include <string.h>#include <stdlib.h>
int main() { int pipefd[2]; pid_t pid;
// Create pipe if (pipe(pipefd) == -1) { perror("pipe failed"); exit(1); }
// Fork process pid = fork(); if (pid == -1) { perror("fork failed"); exit(1); }
if (pid == 0) { // Child process - writer close(pipefd[0]); // Close read end
printf("Child: Sending message...\n"); write(pipefd[1], "Hello", 5);
close(pipefd[1]); // Close write end printf("Child: Message sent, exiting\n");
} else { // Parent process - reader close(pipefd[1]); // Close write end
char buffer[10]; memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer)); // Initialize buffer
printf("Parent: Waiting for message...\n"); ssize_t bytes_read = read(pipefd[0], buffer, 5);
if (bytes_read > 0) { printf("Parent: Received message: '%s'\n", buffer); } else { printf("Parent: Failed to read message\n"); }
close(pipefd[0]); // Close read end
// Wait for child to finish wait(NULL); printf("Parent: Child process finished\n"); }
return 0;}OUTPUT
c@c:~/cos3105$ ./message_passingParent: Waiting for message...Child: Sending message...Child: Message sent, exitingParent: Received message: 'Hello'Parent: Child process finishedNamed Pipes
Section titled “Named Pipes”- Write
#include <stdio.h>#include <sys/stat.h>#include <fcntl.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <string.h>
int main() { mkfifo("/tmp/mypipe", 0666);
int fd = open("/tmp/mypipe", O_WRONLY); write(fd, "Hello from writer!", 18); close(fd);
printf("Message sent\n"); return 0;}OUTPUT
c@c:~/cos3105$ ./writerMessage sent- Read
#include <stdio.h>#include <fcntl.h>#include <unistd.h>
int main() { char buffer[100];
int fd = open("/tmp/mypipe", O_RDONLY); read(fd, buffer, 18); close(fd);
printf("Message received: %s\n", buffer);
// Clean up unlink("/tmp/mypipe");
return 0;}OUTPUT
c@c:~/cos3105$ ./readerMessage received: Hello from writer!Message Queues
Section titled “Message Queues”- For send/receive for message queues, it needs to create key and id for distinguish messages.
-
Generate a Key (
ftok()) that is a unique identifier for multple processes can share.key_t key = ftok(path, proj_id); -
Get/Create Message Queue ID (
msgget())int msgid = msgget(key, 0666 | IPC_CREAT); -
Send message
#include<stdlib.h>#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>#include<unistd.h>#include<sys/types.h>#include<sys/ipc.h>#include<sys/msg.h>#define MAX_TEXT 512struct msgbuf {long mtype; /* message type, must be > 0 */char mtext[MAX_TEXT]; /* message data */};int main(){struct msgbuf message;key_t key = ftok(".", 'A');if (key == -1) {perror("ftok failed");return 1;}int msgid = msgget(key, 0666 | IPC_CREAT);if (msgid == -1) {perror("msgget failed");return 1;}strcpy(message.mtext,"Test Message Queue");message.mtype = 1; // message typeif(msgsnd(msgid,(void *)&message, MAX_TEXT,0)==-1) // msgsnd returns -1 if the message is not sent{perror("msgsnd failed");return 1;}return 0;} -
Check message queues
Terminal window c@c:~/cos3105/lab3_module$ ipcs -q------ Message Queues --------key msqid owner perms used-bytes messages0x41000272 2 c 666 1536 1 -
Receive message
#include<stdlib.h>#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>#include<unistd.h>#include<sys/types.h>#include<sys/ipc.h>#include<sys/msg.h>#define MAX_TEXT 512struct msgbuf {long mtype; /* message type, must be > 0 */char mtext[MAX_TEXT]; /* message data */};int main(){struct msgbuf message;key_t key = ftok(".", 'A');if (key == -1) {perror("ftok failed");return 1;}int msgid = msgget(key, 0666 | IPC_CREAT);if (msgid == -1) {perror("msgget failed");return 1;}// Pick message queue that msg_type = 1if(msgrcv(msgid, &message, sizeof(message.mtext), 1, 0)==-1){perror("msgrcv failed");return 1;}printf("Received: %s\n",message.mtext);return 0;}OUTPUT
Terminal window c@c:~/cos3105$ ./testReceived: Test Message Queue -
Check message queues
Terminal window c@c:~/cos3105/lab3_module$ ipcs -q------ Message Queues --------key msqid owner perms used-bytes messages0x41000272 2 c 666 0 0
Socket
Section titled “Socket”Socket File
Section titled “Socket File”- Server
Server waiting for connection...Client connected!Received: Hello from client!OUTPUT
c@c:~/cos3105$ ./socket_file_serverServer waiting for connection...Client connected!Received: Hello from client!- Client
#include <stdio.h>#include <sys/socket.h>#include <sys/un.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <string.h>
int main() { int client_fd; struct sockaddr_un addr; char buffer[100];
// Create socket client_fd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
// Setup address addr.sun_family = AF_UNIX; strcpy(addr.sun_path, "/tmp/simple_socket");
// Connect to server connect(client_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&addr, sizeof(addr)); printf("Connected to server!\n");
// Send message send(client_fd, "Hello from client!", 18, 0);
// Receive response recv(client_fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0); printf("Server said: %s\n", buffer);
// Cleanup close(client_fd);
return 0;}OUTPUT
Connected to server!Server said: Hello from server!Network Socket
Section titled “Network Socket”#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/socket.h>#include <netinet/in.h>#include <arpa/inet.h>#include <netdb.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <errno.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <time.h>
int main() { printf("Configuring local address...\n"); struct addrinfo hints; memset(&hints, 0, sizeof(hints)); hints.ai_family = AF_INET; hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM; hints.ai_flags = AI_PASSIVE;
struct addrinfo *bind_address; if (getaddrinfo(0, "3030", &hints, &bind_address) != 0) { fprintf(stderr, "getaddrinfo() failed.\n"); return 1; }
printf("Creating socket...\n"); int socket_listen; socket_listen = socket(bind_address->ai_family, bind_address->ai_socktype, bind_address->ai_protocol); if (socket_listen < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "socket() failed. (%d)\n", errno); freeaddrinfo(bind_address); return 1; }
// Enable address reuse to avoid "Address already in use" error int yes = 1; if (setsockopt(socket_listen, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &yes, sizeof(yes)) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "setsockopt() failed. (%d)\n", errno); close(socket_listen); freeaddrinfo(bind_address); return 1; }
printf("Binding socket to local address...\n"); if (bind(socket_listen, bind_address->ai_addr, bind_address->ai_addrlen)) { fprintf(stderr, "bind() failed. (%d)\n", errno); close(socket_listen); freeaddrinfo(bind_address); return 1; } freeaddrinfo(bind_address);
printf("Listening...\n"); if (listen(socket_listen, 10) < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "listen() failed. (%d)\n", errno); close(socket_listen); return 1; }
printf("Waiting for connection...\n"); struct sockaddr_storage client_address; socklen_t client_len = sizeof(client_address); int socket_client = accept(socket_listen, (struct sockaddr*) &client_address, &client_len); if (socket_client < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "accept() failed. (%d)\n", errno); close(socket_listen); return 1; }
printf("Client is connected... "); char address_buffer[100]; if (getnameinfo((struct sockaddr*)&client_address, client_len, address_buffer, sizeof(address_buffer), 0, 0, NI_NUMERICHOST) == 0) { printf("%s\n", address_buffer); } else { printf("unknown\n"); }
printf("Reading request...\n"); char request[1024]; int bytes_received = recv(socket_client, request, sizeof(request) - 1, 0); if (bytes_received > 0) { printf("Received %d bytes.\n", bytes_received); request[bytes_received] = '\0'; // Null terminate for safety // Uncomment the next line if you want to see the request // printf("Request: %.*s", bytes_received, request); } else { printf("Failed to receive data or connection closed.\n"); close(socket_client); close(socket_listen); return 1; }
printf("Sending response...\n");
// Get time first time_t timer; time(&timer); char *time_msg = ctime(&timer);
// Calculate content length (remove newline from ctime) int time_len = strlen(time_msg); if (time_len > 0 && time_msg[time_len - 1] == '\n') { time_msg[time_len - 1] = '\0'; // Remove trailing newline time_len--; }
char response_buffer[1024]; int content_length = strlen("Local time is: ") + time_len;
// Build complete HTTP response with proper Content-Length header int response_len = snprintf(response_buffer, sizeof(response_buffer), "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n" "Connection: close\r\n" "Content-Type: text/plain\r\n" "Content-Length: %d\r\n" "\r\n" "Local time is: %s", content_length, time_msg);
int bytes_sent = send(socket_client, response_buffer, response_len, 0); printf("Sent %d of %d bytes.\n", bytes_sent, response_len);
printf("Closing connection...\n"); close(socket_client);
printf("Closing listening socket...\n"); close(socket_listen);
printf("Finished.\n"); return 0;}OUTPUT
c@c:~/cos3105$ curl localhost:3030Local time is: Sun Sep 7 12:53:56 2025- OR open in browser http://localhost:8080/proxy/3030/
Chat Server vs. Client
Section titled “Chat Server vs. Client”- Server
/* * MIT License * * Copyright (c) 2018 Lewis Van Winkle * * Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy * of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal * in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights * to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell * copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is * furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions: * * The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all * copies or substantial portions of the Software. * * THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR * IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE * AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER * LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, * OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE * SOFTWARE. */
#define _POSIX_C_SOURCE 200112L#define _DEFAULT_SOURCE#define _BSD_SOURCE
#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/socket.h>#include <netinet/in.h>#include <arpa/inet.h>#include <netdb.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <errno.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <ctype.h>#include <stdlib.h>
#define ISVALIDSOCKET(s) ((s) >= 0)#define CLOSESOCKET(s) close(s)#define SOCKET int#define GETSOCKETERRNO() (errno)
int main() { printf("Configuring local address...\n"); struct addrinfo hints; memset(&hints, 0, sizeof(hints)); hints.ai_family = AF_INET; hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM; hints.ai_flags = AI_PASSIVE;
struct addrinfo *bind_address; getaddrinfo(0, "3030", &hints, &bind_address);
printf("Creating socket...\n"); SOCKET socket_listen; socket_listen = socket(bind_address->ai_family, bind_address->ai_socktype, bind_address->ai_protocol); if (!ISVALIDSOCKET(socket_listen)) { fprintf(stderr, "socket() failed. (%d)\n", GETSOCKETERRNO()); return 1; }
// Allow socket address reuse int yes = 1; if (setsockopt(socket_listen, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &yes, sizeof(yes)) < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "setsockopt() failed. (%d)\n", GETSOCKETERRNO()); return 1; }
printf("Binding socket to local address...\n"); if (bind(socket_listen, bind_address->ai_addr, bind_address->ai_addrlen)) { fprintf(stderr, "bind() failed. (%d)\n", GETSOCKETERRNO()); return 1; } freeaddrinfo(bind_address);
printf("Listening...\n"); if (listen(socket_listen, 10) < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "listen() failed. (%d)\n", GETSOCKETERRNO()); return 1; }
printf("Waiting for connections...\n"); while(1) { struct sockaddr_storage client_address; socklen_t client_len = sizeof(client_address); SOCKET socket_client = accept(socket_listen, (struct sockaddr*) &client_address, &client_len); if (!ISVALIDSOCKET(socket_client)) { fprintf(stderr, "accept() failed. (%d)\n", GETSOCKETERRNO()); return 1; }
char address_buffer[100]; getnameinfo((struct sockaddr*)&client_address, client_len, address_buffer, sizeof(address_buffer), 0, 0, NI_NUMERICHOST); printf("New connection from %s\n", address_buffer);
int pid = fork(); if (pid == 0) { //child process CLOSESOCKET(socket_listen); while(1) { char read[1024]; int bytes_received = recv(socket_client, read, 1024, 0); if (bytes_received < 1) { CLOSESOCKET(socket_client); exit(0); } int j; for (j = 0; j < bytes_received; ++j) read[j] = toupper(read[j]); send(socket_client, read, bytes_received, 0); } } CLOSESOCKET(socket_client); } //while(1)
printf("Closing listening socket...\n"); CLOSESOCKET(socket_listen); printf("Finished.\n"); return 0;}- Client
#define _POSIX_C_SOURCE 200112L#define _DEFAULT_SOURCE#define _BSD_SOURCE
#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/socket.h>#include <sys/select.h>#include <netinet/in.h>#include <arpa/inet.h>#include <netdb.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <errno.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <ctype.h>
#define ISVALIDSOCKET(s) ((s) >= 0)#define CLOSESOCKET(s) close(s)#define SOCKET int#define GETSOCKETERRNO() (errno)
int main() { printf("Connecting to server...\n");
struct addrinfo hints; memset(&hints, 0, sizeof(hints)); hints.ai_family = AF_INET; hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM;
struct addrinfo *peer_address; if (getaddrinfo("127.0.0.1", "3030", &hints, &peer_address)) { fprintf(stderr, "getaddrinfo() failed.\n"); return 1; }
SOCKET socket_peer; socket_peer = socket(peer_address->ai_family, peer_address->ai_socktype, peer_address->ai_protocol); if (!ISVALIDSOCKET(socket_peer)) { fprintf(stderr, "socket() failed. (%d)\n", GETSOCKETERRNO()); return 1; }
if (connect(socket_peer, peer_address->ai_addr, peer_address->ai_addrlen)) { fprintf(stderr, "connect() failed. (%d)\n", GETSOCKETERRNO()); return 1; } freeaddrinfo(peer_address);
printf("Connected. Type messages to send (Ctrl+C to quit):\n");
fd_set master; FD_ZERO(&master); FD_SET(socket_peer, &master); FD_SET(0, &master); // stdin SOCKET max_socket = socket_peer;
while(1) { fd_set reads; reads = master; if (select(max_socket+1, &reads, 0, 0, 0) < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "select() failed. (%d)\n", GETSOCKETERRNO()); return 1; }
if (FD_ISSET(socket_peer, &reads)) { char read[4096]; int bytes_received = recv(socket_peer, read, 4096, 0); if (bytes_received < 1) { printf("Connection closed by peer.\n"); break; } printf("Received: %.*s", bytes_received, read); }
if (FD_ISSET(0, &reads)) { char read[4096]; if (!fgets(read, 4096, stdin)) break; printf("Sending: %s", read); int bytes_sent = send(socket_peer, read, strlen(read), 0); if (bytes_sent < 1) { printf("send() failed.\n"); break; } } }
printf("Closing socket...\n"); CLOSESOCKET(socket_peer); printf("Finished.\n"); return 0;}OUTPUT
- Sever
c@c:~/cos3105/network_server$ make rungcc -Wall -Wextra -std=c99 -c src/server.c -o obj/server.og++ -o bin/server obj/server.o./bin/serverConfiguring local address...Creating socket...Binding socket to local address...Listening...Waiting for connections...New connection from 127.0.0.1- Client
c@c:~/cos3105/network_client$ make run./bin/clientConnecting to server...Connected. Type messages to send (Ctrl+C to quit):testSending: testReceived: TESTAAAASending: AAAAReceived: AAAA- Server
#include <stdio.h>#include <sys/socket.h>#include <sys/un.h>#include <unistd.h>
struct rpc_data { int a, b, result;};
int main() { int server_fd, client_fd; struct sockaddr_un addr; struct rpc_data data;
// Create socket server_fd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
// Setup address addr.sun_family = AF_UNIX; strcpy(addr.sun_path, "/tmp/rpc"); unlink("/tmp/rpc");
// Bind and listen bind(server_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&addr, sizeof(addr)); listen(server_fd, 1);
printf("RPC Server ready\n");
// Accept client client_fd = accept(server_fd, NULL, NULL);
// Receive parameters recv(client_fd, &data, sizeof(data), 0); printf("Received: %d + %d\n", data.a, data.b);
// Do calculation (this is the "remote" function) data.result = data.a + data.b;
// Send result back send(client_fd, &data, sizeof(data), 0); printf("Sent result: %d\n", data.result);
close(client_fd); close(server_fd); unlink("/tmp/rpc");
return 0;}OUTPUT
c@c:~/cos3105$ ./rpc_serverRPC Server readyReceived: 10 + 5Sent result: 15- Client
#include <stdio.h>#include <sys/socket.h>#include <sys/un.h>#include <unistd.h>
struct rpc_data { int a, b, result;};
// This function looks local but actually calls remote serverint remote_add(int x, int y) { int sockfd; struct sockaddr_un addr; struct rpc_data data;
// Connect to server sockfd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0); addr.sun_family = AF_UNIX; strcpy(addr.sun_path, "/tmp/rpc"); connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&addr, sizeof(addr));
// Send parameters data.a = x; data.b = y; send(sockfd, &data, sizeof(data), 0);
// Get result recv(sockfd, &data, sizeof(data), 0);
close(sockfd); return data.result;}
int main() { printf("RPC Client\n");
// This looks like a normal function call! int result = remote_add(10, 5);
printf("10 + 5 = %d\n", result);
return 0;}OUTPUT
c@c:~/cos3105$ ./rpc_clientRPC Client10 + 5 = 15Producer/Consumer (Race condition)
Section titled “Producer/Consumer (Race condition)”Not use all buffer
Section titled “Not use all buffer”#include <stdio.h>#include <sys/mman.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <sys/wait.h>#include <stdbool.h>#define ARRAY_SIZE 5struct Item { int buffers[ARRAY_SIZE]; int in; int out;};int main() { // Create shared array struct Item *shared_items = mmap(NULL, sizeof(struct Item), PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED | MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0);
if (fork() == 0) { // Child process int value = 10; while(true){ while((shared_items->in + 1) % ARRAY_SIZE == shared_items->out); printf("produce: %d\n", value); shared_items->buffers[shared_items->in] = value; shared_items->in = (shared_items->in + 1) % ARRAY_SIZE; value+=10; sleep(1); }
}else { // Parent process sleep(1); while(true){ while(shared_items->in == shared_items->out); int value = shared_items->buffers[shared_items->out]; printf("consume: %d\n", value); shared_items->out = (shared_items->out + 1) % ARRAY_SIZE; sleep(1); } wait(NULL); // Wait for child munmap(shared_items, sizeof(struct Item)); }
return 0;}Use all buffer
Section titled “Use all buffer”#include <stdio.h>#include <sys/mman.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <sys/wait.h>#include <stdbool.h>
#define ARRAY_SIZE 5struct Item { int buffers[ARRAY_SIZE]; int in; int out; int counter;};int main() { // Create shared array struct Item *shared_items = mmap(NULL, sizeof(struct Item), PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED | MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0);
if (fork() == 0) { // Child process int value = 10; while(true){ while(shared_items->counter == ARRAY_SIZE); printf("produce: %d\n", value); shared_items->buffers[shared_items->in] = value; shared_items->in = (shared_items->in + 1) % ARRAY_SIZE; shared_items->counter = shared_items->counter+1; value+=10; // sleep(3); }
}else { // Parent process // sleep(1); while(true){ while(shared_items->counter == 0); int value = shared_items->buffers[shared_items->out]; printf("consume: %d\n", value); shared_items->out = (shared_items->out + 1) % ARRAY_SIZE; shared_items->counter = shared_items->counter-1; // sleep(1); }
wait(NULL); // Wait for child munmap(shared_items, sizeof(struct Item)); }
return 0;}OUTPUT
consume: 1042170produce: 1042210consume: 1042180produce: 1042220consume: 1042190produce: 1042230consume: 1042200produce: 1042240consume: 1042210produce: 1042250consume: 1042220produce: 1042260consume: 1042230produce: 1042270consume: 1042240produce: 1042280consume: 1042250