#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <malloc.h> // for malloc_usable_size (GNU extension)
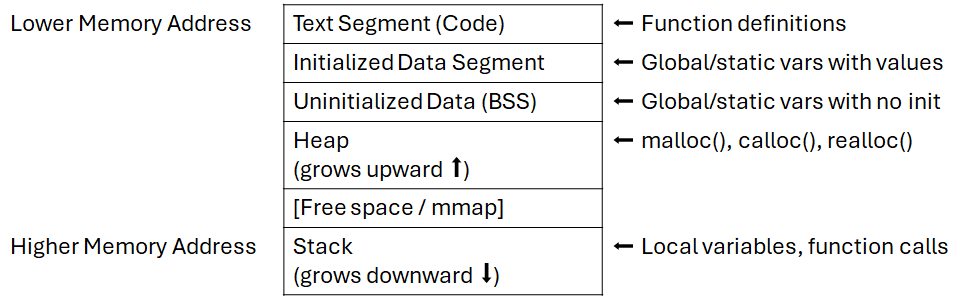
int global_var = 100; // Global variablestatic int static_global_var = 200; // Static global variable
void show_memory_layout() { int stack_var = 300; // Local (stack) variable static int static_local_var = 400; // Static local variable int *heap_var = malloc(50 * sizeof(int)); // Heap allocation
// Write something to heap to prevent compiler optimization for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) heap_var[i] = i;
printf("\n=== MEMORY LAYOUT ===\n");
// Code address printf("Code (function): %p\n", (void *)show_memory_layout);
// Global / static printf("Global var: %p (size: %zu bytes)\n", (void *)&global_var, sizeof(global_var)); printf("Static global var: %p (size: %zu bytes)\n", (void *)&static_global_var, sizeof(static_global_var));
// Heap printf("Heap var (malloc): %p (requested: %zu bytes, actual: %zu bytes)\n", (void *)heap_var, 50 * sizeof(int), malloc_usable_size(heap_var));
// Stack printf("Stack var (local): %p (size: %zu bytes)\n", (void *)&stack_var, sizeof(stack_var)); printf("Static local var: %p (size: %zu bytes)\n", (void *)&static_local_var, sizeof(static_local_var));
printf("======================\n");
free(heap_var); // Clean up}
int main() { show_memory_layout(); return 0;}OUTPUT
c@c:~/cos3105$ ./memory_layout
=== MEMORY LAYOUT ===Code (function): 0x5cb6d9cbe1e9Global var: 0x5cb6d9cc1010 (size: 4 bytes)Static global var: 0x5cb6d9cc1014 (size: 4 bytes)Heap var (malloc): 0x5cb718c1f2a0 (requested: 200 bytes, actual: 200 bytes)Stack var (local): 0x7ffdb5b83568 (size: 4 bytes)Static local var: 0x5cb6d9cc1018 (size: 4 bytes)======================